EEG Therapy for Insomnia
Electroencephalogram (EEG) therapy is an emerging treatment for insomnia. This article explores its effectiveness, focusing on EEG-based therapies and their impact on sleep disorders.
EEG Biofeedback: Enhancing Sleep Quality
A recent study, “EEG Biofeedback Decreases Theta and Beta Power While Increasing Alpha Power in Insomniacs: An Open-Label Study,” shows promising results. Researchers found that EEG biofeedback can alter brain wave patterns. Specifically, it reduces theta and beta power and increases alpha power. These changes improved sleep quality. Insomniacs who underwent EEG biofeedback reported falling asleep faster and enjoying deeper sleep.
Z-Score Neurofeedback: Targeted Brain Training
Z-Score neurofeedback is another practical approach for treating insomnia. This method uses real-time EEG data to provide precise feedback. It aims to normalize brain function by comparing it to a healthy standard (z-score). Studies show that Z-Score neurofeedback can significantly reduce insomnia symptoms. Patients often experience fewer awakenings during the night and improved overall sleep quality.
Non-Linear Neurofeedback: Addressing Insomnia and Anxiety
Non-linear neurofeedback offers a non-invasive way to treat insomnia and anxiety. This therapy focuses on optimizing brain function without diagnosing specific issues. It uses EEG data to train the brain to self-correct. Many patients report reduced anxiety and better sleep after several sessions. Neuroptimal neurofeedback is gaining popularity due to its gentle and holistic approach.
Comparing Neurofeedback and Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
A pilot study, “A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Neurofeedback and Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia Patients,” provides insights into the effectiveness of neurofeedback compared to cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). In this study, participants were assigned to either neurofeedback or CBT. Both cohorts showed significant improvements in sleep quality. However, the neurofeedback group experienced faster results. They reported better sleep efficiency and reduced sleep latency sooner than the CBT group. This study suggests that neurofeedback can be a viable alternative or complement to traditional CBT for insomnia. It highlights neurofeedback’s potential to provide quicker relief for patients with sleep disorders.
EEG Therapy for HIV Patients with Insomnia
Insomnia is a common issue for HIV patients. The study “Evaluation of the Effect of Neurofeedback on Polysomnographic Changes and Improvement in the Life Quality of People with HIV with Sleep Disorders: A Clinical Trial Study” provides valuable insights. Researchers found that EEG therapy can improve sleep patterns and life quality in HIV patients. Participants reported longer sleep duration and fewer disturbances. This therapy also positively impacted their overall well-being and mental health.
Neurofeedback Training
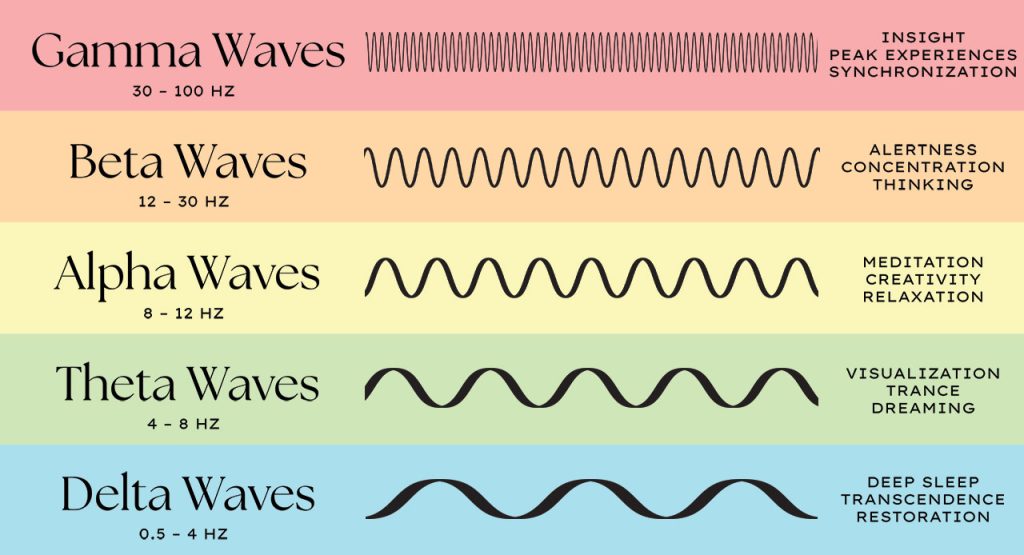
In the neurofeedback system, linked ears were used with an active electrode at Oz (occipital midline). Subjects heard a tone when their alpha frequency (12-15 Hz) surpassed their initial testing frequency (2 minutes with eyes open). Continuous monitoring ensured subjects didn’t fall asleep. If the EEG showed signs of sleep, the investigator reminded the subject to focus on the tone. When subjects maintained an alpha amplitude double their baseline for 20 minutes, the reward tone shifted to a slightly lower frequency (low beta, 4-8 Hz, high theta, 25-30 Hz). Training sessions continued for 16 weeks.
Broader Benefits of EEG Therapy
EEG therapy offers numerous benefits for a variety of conditions beyond insomnia. It has shown effectiveness in treating anxiety, adult and child ADHD, and more. Unlike pharmaceuticals, which can carry severe side effects and often lack long-term efficacy, EEG therapy presents a safer and more sustainable alternative. Medications for anxiety and ADHD, for example, can lead to dependency and other health issues over time. In contrast, EEG therapy aims to retrain the brain, promoting lasting improvements without the risk of addiction or adverse effects.
Additionally, EEG therapy is non-invasive and customizable, allowing for personalized treatment plans that address specific brain activity patterns. This customized approach ensures that each patient receives the most effective intervention for their unique condition. As research continues to validate its benefits, EEG therapy could revolutionize the way we treat a range of neurological and psychological disorders, offering hope for long-term relief without the drawbacks of conventional medications.
Conclusion
EEG therapy presents a promising solution for insomnia. Each method offers unique benefits, from EEG biofeedback to Z-Score neurofeedback and Neuroptimal neurofeedback. EEG therapy’s potential to improve sleep in HIV patients highlights its versatility. As research continues, EEG therapy may become a standard treatment for insomnia and related conditions.
References:
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/human-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnhum.2018.00142/full
https://shorturl.at/VrANp
https://openaidsjournal.com/VOLUME/18/ELOCATOR/e18746136268741/FULLTEXT/