Brainwave Chart: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Human brainwaves are electrical impulses in the brain, measured in cycles per second or Hertz (Hz). These brainwaves are crucial to understanding how the brain functions, reacts and interacts with the body and the environment. With advancements in neuroscience, the study of brainwaves has expanded, revealing fascinating insights into cognitive processes, consciousness, and even the nature of reality. This article delves into the latest scientific knowledge on human brainwaves, explores the intriguing holographic theory, examines brainwave differences across age groups and species, and answers common questions about this captivating subject.
Latest Scientific Knowledge on Human Brainwaves
Understanding Brainwaves
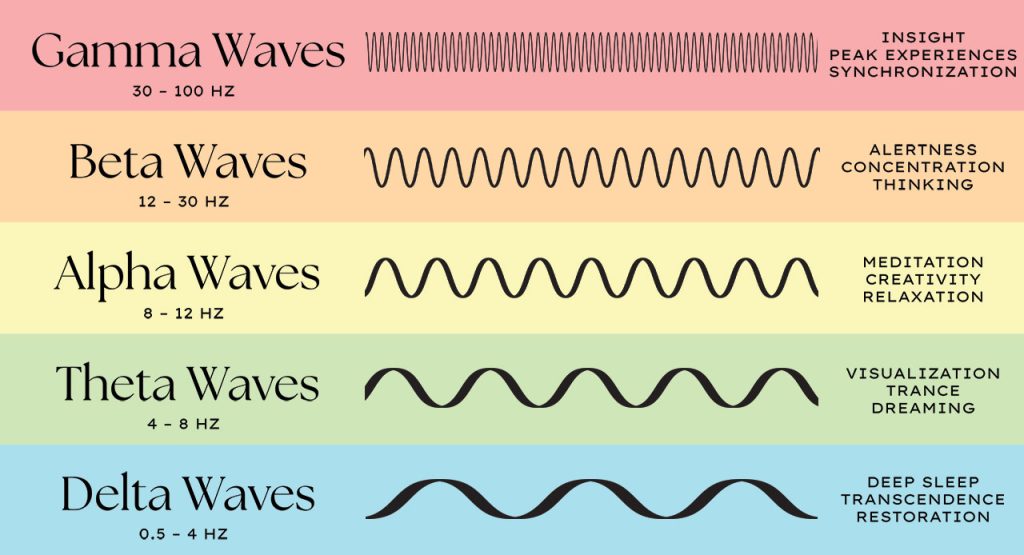
Brainwaves are categorized into five main types based on their frequency ranges:
- Delta Waves (0.5-4 Hz): These are the slowest brainwaves associated with deep sleep and therapeutic processes.
- Theta Waves (4-8 Hz): Linked to light sleep, relaxation, and meditation.
- Alpha Waves (8-12 Hz): Present during calm, relaxed, but awake states, often seen during meditation and daydreaming.
- Beta Waves (12-30 Hz): Associated with active thinking, problem-solving, and concentration.
- Gamma Waves (30-100 Hz): The fastest brainwaves, linked to high-level cognitive functioning, information processing, and perception.
Advances in Brainwave Research
Recent studies have shown that brainwaves are crucial in communication between different brain regions. This synchronization allows for coordinated activities, such as memory formation and retrieval, decision-making, and emotional regulation. Techniques like electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG) have advanced our understanding by providing detailed maps of brainwave activities.
Brainwaves and Holographic Theory
The holographic theory of the brain posits that our brains process information like holograms, where every part of the hologram contains information about the whole. This theory suggests that memories and information are distributed throughout the brain rather than localized in specific regions.
Brainwaves in the Holographic Model
Brainwaves are integral to this holographic processing. Gamma waves, in particular, are believed to facilitate information integration across different brain regions, supporting the idea that our perception of reality is a unified, coherent experience constructed from diverse neural inputs.
Differences in Brainwave Structures: Infants, Children, and Adults
Infants
Brainwaves in infants are predominantly in the delta range, reflecting the high amount of deep sleep necessary for growth and development. Slower rhythms and less complex waveforms also characterize their brain activity.
Children
Theta waves become more prominent as children grow, especially during play and daydreaming. Alpha waves start to emerge, indicating increasing alertness and cognitive engagement.
Adults
In adults, beta waves dominate during waking hours, reflecting active thinking and problem-solving. Gamma waves are more frequent, indicating mature and efficient cognitive processing. The complexity and synchronization of brainwaves are also more advanced than those of children and infants.
Human Brainwaves vs. Other Mammals
Similarities
Many mammals exhibit brainwave patterns similar to those of humans, with delta, theta, alpha, and beta waves present. These patterns are associated with identical states of consciousness, such as sleep, relaxation, and alertness.
Differences
The primary difference lies in the complexity and frequency of gamma waves. Humans have a higher frequency of gamma waves, reflecting advanced cognitive abilities like abstract thinking, language, and complex problem-solving. While exhibiting gamma waves, other mammals tend to have less frequency and complexity, correlating with their cognitive capabilities.
FAQ
- What are brainwaves?
Brainwaves are electrical impulses in the brain, categorized by frequency into delta, theta, alpha, beta, and gamma waves.
- How are brainwaves measured?
Brainwaves are measured using EEG (electroencephalography) and MEG (magnetoencephalography), which detect electrical activity in the brain.
- What is the role of gamma waves?
Gamma waves are associated with high-level cognitive functions, including perception, information processing, and consciousness integration.
- How do brainwaves change with age?
Infants primarily have delta waves, children exhibit more theta and alpha waves, and adults have prominent beta and gamma waves, reflecting cognitive development and complexity.
- What is the holographic theory of the brain?
The holographic theory suggests that the brain processes information in a distributed manner, similar to how a hologram stores information across its entire structure.
- Do other mammals have the same brainwaves as humans?
Yes, other mammals exhibit similar brainwave patterns. Still, the complexity and frequency, especially of gamma waves, are generally lower compared to humans.
- Can brainwaves be altered or controlled?
Neurofeedback and meditation can influence brainwave patterns, potentially enhancing cognitive functions and emotional regulation.
- Are Gamma brainwaves associated with the progression of Dementia and Alzheimer’s?
There is convincing evidence that patients with declining cognitive skills and memory also have a deficiency of gamma in their EEG structures.
Gamma-based neurofeedback training has also shown improvements in low gamma ratios among people with dementia.
A reduction in deep-stage sleep in seniors also correlates to the progression of Alzheimer’s. Improving deep sleep is vital to keeping the brain fit into old age.
Conclusion
The study of brainwaves offers profound insights into the workings of the human mind, revealing the intricacies of cognitive processes, consciousness, and the potential holographic nature of our brain’s information processing. Understanding the differences in brainwave structures across age groups and species highlights the unique aspects of human cognition. As neuroscience advances, our comprehension of brainwaves grows, promising new ways to enhance mental health and cognitive abilities.